Building classes, special constructions and fire protection
The fire protection and stability of buildings in Germany is generally regulated in the "Musterbauordnung" (short MBO, model building code). However, each federal state still has its own state building code (e.g. BauO NRW), which must also be taken into account. In the building regulations, the respective building classes specify what must be taken into account from a fire protection point of view. If a building cannot be assigned to any building class, it is a special construction where individual requirements may exist. In this blog article, we give you a clear overview of the defined building classes, the fire protection requirements and what belongs to special buildings.
Regulation – model building code
The general model building code regulates the standard and minimum construction of structures and construction products. Specific requirements beyond this may exist due to the state building regulations of the federal states. The purpose is to arrange, erect, modify and maintain installations in such a way that public safety and order are not endangered.

Standard and special construction

From the point of view of fire protection, buildings are colloquially divided into two types:
- Standard construction
- Special construction
The building classes basically refer to a standard construction and are based on the model building code. Special constructions are buildings with a special type or use and are subject to special requirements, more on this later.
Meaning and purpose of building classes
The fire protection in a building is intended to protect the building itself, but also surrounding buildings in the neighborhood. The higher the risk that other parts of the building or neighbouring buildings can be affected, the higher the building class. A detached single-family house, for example, has a lower risk potential than a multi-storey residential building.

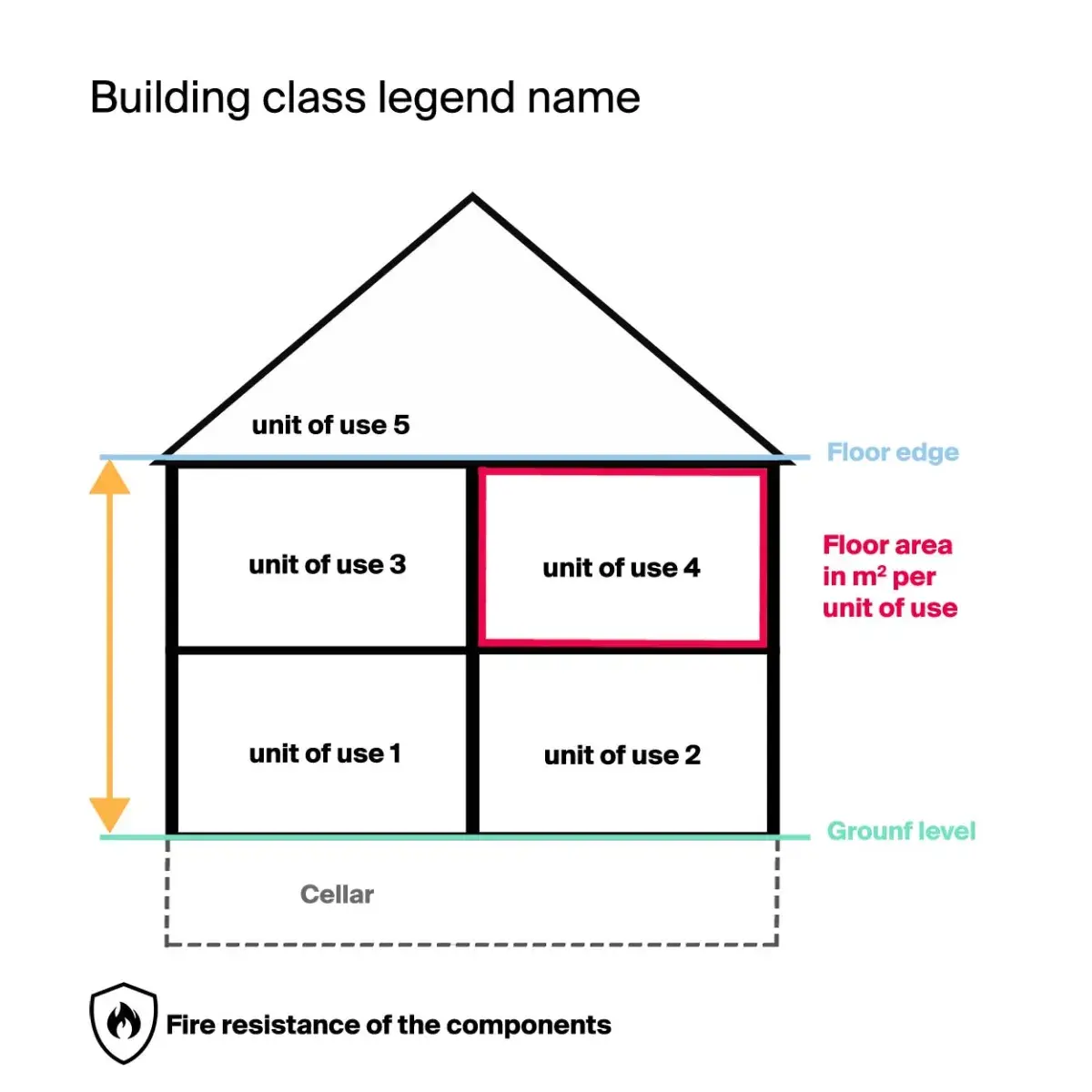
Definition of building classes
Building classes are regulated in §2 of the Model Building Code. Five building classes are defined, which are categorised according to height and extent - the units of use and the gross total area. The classification of buildings into classes provides information about the fire protection requirements, e.g. which building materials may be used. Je höher das Gebäude einer Klasse eingestuft worden ist, desto höher sind die Anforderungen. Die steigenden Anforderungen hängen mit dem steigenden Gefahrenpotential zusammen. The higher the building of a class, the higher the requirements. The increasing requirements are related to the increasing risk potential.
Determination of the height for classification in a building class
The height of a building is calculated from the terrain surface to the top of the floor.
Determination of the unit of use for classification in a building class
A usage unit is a fixed area, such as a residential unit or an office unit. The number or size of the rooms does not matter at first. The gross total floor area of the usage unit is decisive for the classification in the building class. The gross floor area is the total built-up area above the foundation including walls.
Fire protection for building classes and special constructions
Do you have any questions and would you like advice on fire protection for building classes or special constructions? Our regional experts will be happy to assist you.
Difference between building materials and components
What are building materials and what must be taken into account with regard to fire protection?
Building materials are the basic material to create a structure, such as concrete, cement, steel.
- Non-combustible building materials: building material class A1, A2 e.g. sand, gravel, clay
- Flame retardant building materials: Building material class B1 e.g. wood wool lightweight panels, plasterboard, PVC pipes
- Normally flammable building materials: building material class B2 e.g. wood, plasterboard composite board
- Highly flammable building materials: Building material class B3 e.g. straw, untreated sheep's wool
What are building parts and what must be taken into account with regard to fire protection?
Components are made of building materials, e.g. walls, ceilings, columns, stairs.
- Fire-resistant components: minimum 90 min. fire resistance
- Highly fire-retardant components: minimum 60 min. fire resistance
- Fire-retardant components: at least 30 min. fire resistance
Overview of building classes according to MBO (2020)
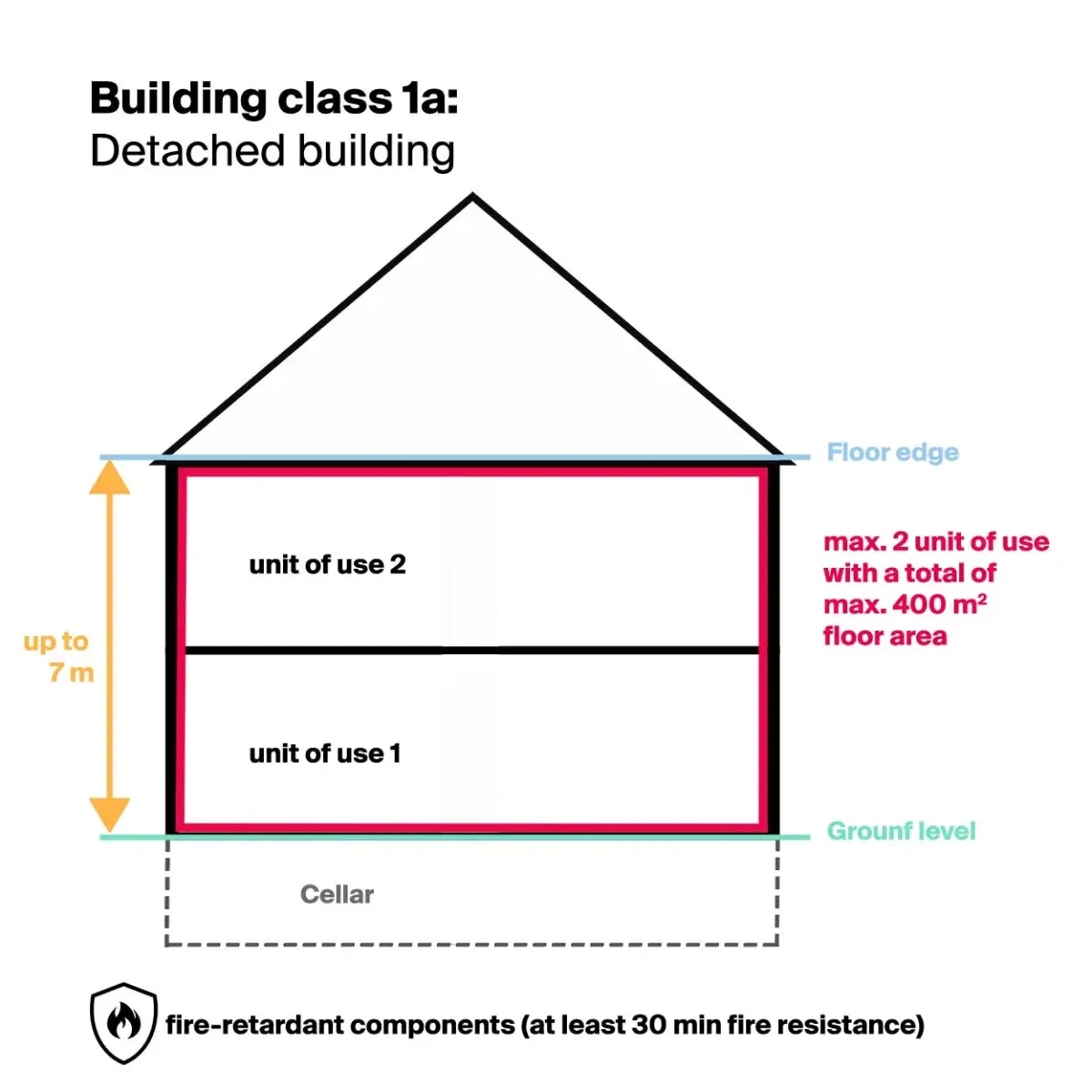
Building class 1a
Building class 1a "Detached buildings" includes, for example, single-family homes.
Building calculation
- Hazard potential: very low
- Height: max. 7 m
- Usage units: max. 2, which have a total floor area of no more than 400 m2
Fire protection requirement
- Components: fire-retardant
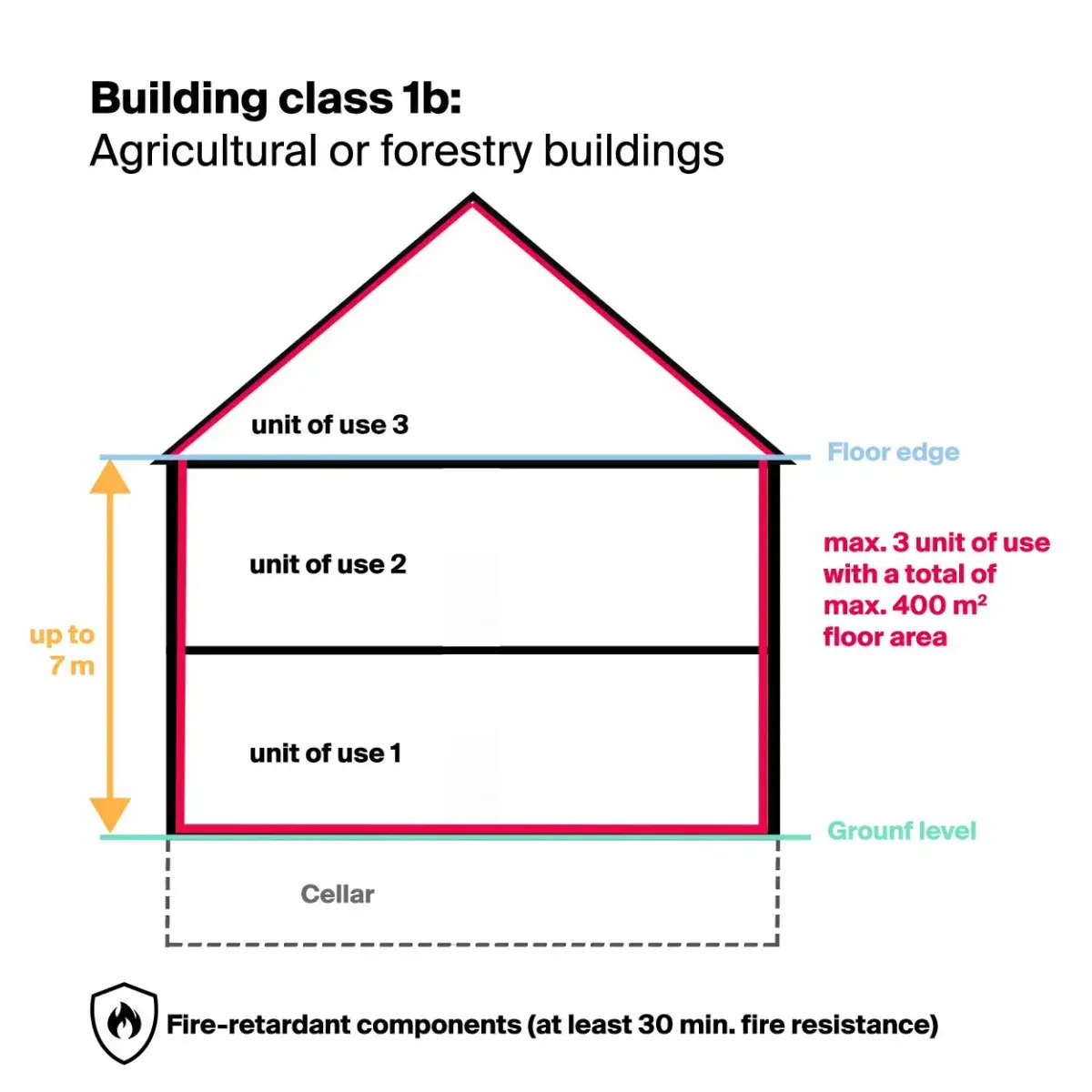
Building class 1b
Building class 1b "Freestanding agricultural or forestry building" includes, for example, farms.
Building calculation
- Hazard potential: very low
- Height: max. 7 m
- Usage units: max. 2
Fire safety requirements
- Components: fire-retardant
Building class 2
Building class 2 "non-detached buildings" includes, for example, terraced houses, semi-detached houses as well as non-detached buildings.
Building calculation
- Hazard potential: slightly increased
- Height: max. 7 m
- Usage units: more than 2 units with a floor area greater than 400 m2
Fire safety requirements
Components: fire-retardant

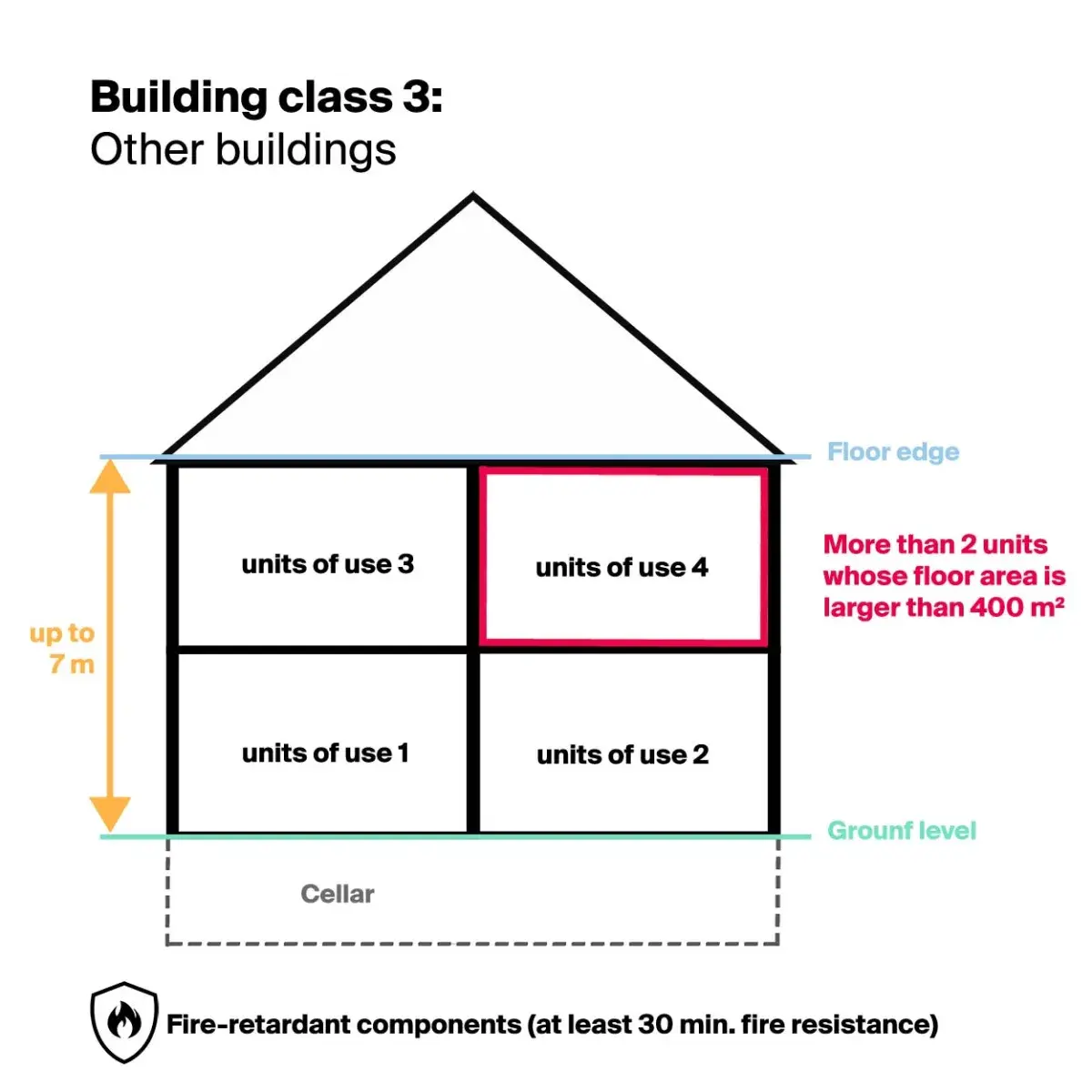
Building class 3
Building class 3 "Other buildings" includes, for example, apartment buildings and commercial properties with offices.
Building calculation
- Hazard potential: slightly increased
- Height: max. 7 m
- Usage units: more than 2 units with a floor area greater than 400 m2
Fire safety requirements
Components: fire-retardant
Building class 4
Building class 4 includes, for example, apartment buildings or commercial properties with offices that are max. 13 m high.
Building calculation
- Hazard potential: high
- Height: max. 13 m
- Usage units: more than 2 units, per unit max. 400 m2 floor area
Fire safety requirements
Components: highly fire retardant

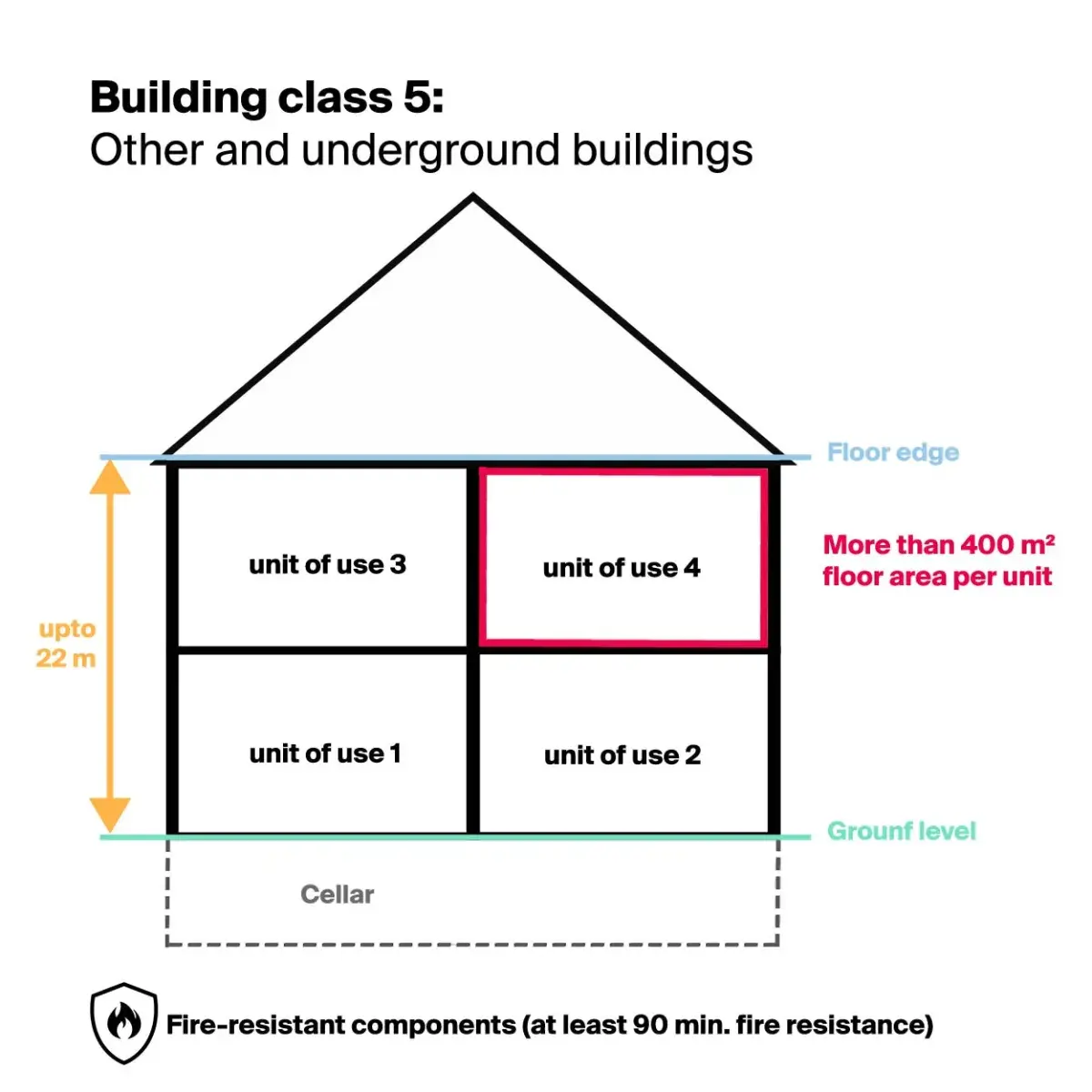
Building class 5
Building class 5 "Other buildings including underground buildings" includes apartment buildings and office complexes up to 22m high.
Building calculation
- Hazard potential: very high
- Height: up to 22 m
- Usage units: more than 400 m2 floor area per non-unit
Fire safety requirements
- Components: fire resistant
Fire protection of building classes
In this blog article, we can only give you a general overview of the fire protection requirements according to MBO. If you have a specific concern and need support, our regional experts are at your disposal.
Special constructions according to MBO
Special constructions are systems and rooms that have a special risk potential due to the use or the sitting. This does not mean a higher risk potential, but a different way of dealing with the danger. A hospital, which is a special construction, represents a special danger due to the number of people or the limited self-rescue ability of the persons, which must be taken into account when planning fire protection measures.


The special construction is subject to special requirements but also simplifications. In part, these requirements and facilitations are regulated, in part, the individual circumstances must be taken into account. In the case of special constructions, however, the requirements of the building class can also be taken into account as a basic requirement. Requirements of the building classes therefore supplement the requirements of the special buildings.
Examples of special constructions:
- High-rise buildings with a height of more than 22 m
- Structural installation (e.g. construction crane) with a height of more than 30 m
- Building with more than 1,600 m² floor area of the floor with the largest extension
- Sales outlets with more than 800 m² floor space
- buildings with rooms for office or administrative use and individually have a floor area of more than 400 m²,
- Buildings with rooms designed for more than 100 people
- Meeting places for more than 200 visitors and outdoors for more than 1000 visitors
- Pubs and restaurants with more than 40 seats in the building or more than 1,000 outdoor guest seats, accommodation restaurants with more than 12 beds, amusement arcades with more than 150 m2
- Building for the care or support of persons with more than 6 persons, intensive care or common escape route for more than 12 persons
- Hospitals
- Facilities for accommodating persons
- Day facilities
- Schools Universities
- Correctional
- Camping and motorhome pitches
- Amusement park
- Rack storage with stored goods over 7.50 m height
- Structures for the use or storage of substances with an explosion or increased fire hazard
- Installations and rooms which have a similar hazard potential as the special constructions to be mentioned above
What is the difference between buildings and structures?
When plants made of construction products are connected to the ground, they are referred to as structural installations. These include, for example, scaffolding, parking spaces for vehicles, amusement parks, campsites, storage areas or landfills (see MBO 2002 §2(1)). Buildings are covered structures that can be used independently and serve to protect people, animals or property (see MBO §2(2)).
What classes of buildings are there?
There are five classes of buildings. They differ in building height and extension. Depending on the classification into a building class, the requirements for fire protection differ. The higher the hazard potential, the higher the specifications for the building materials and components used.
What does fire protection have to do with building class?
For each building class, there are specifications for fire protection, which applies above all to the selection of components and building materials. There are fire-retardant or fire-resistant building materials and building materials that keep smoke or fire from 30 to 180 minutes and thus people, animals and property can be better protected. The higher the risk potential, the higher the requirements for fire protection.
Conclusion on building classes, special constructions and fire protection
In addition to the model building code, the state building code must also be taken into account. Already during the planning of a building, the building class and thus the requirements for fire protection should be taken into account. Fewer square meters or the height make a decisive difference in fire safety requirements! We are happy to advise or execute at your side.
